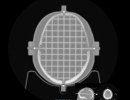
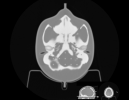
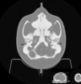
MRI Distortion Phantom for SRS Model 603A
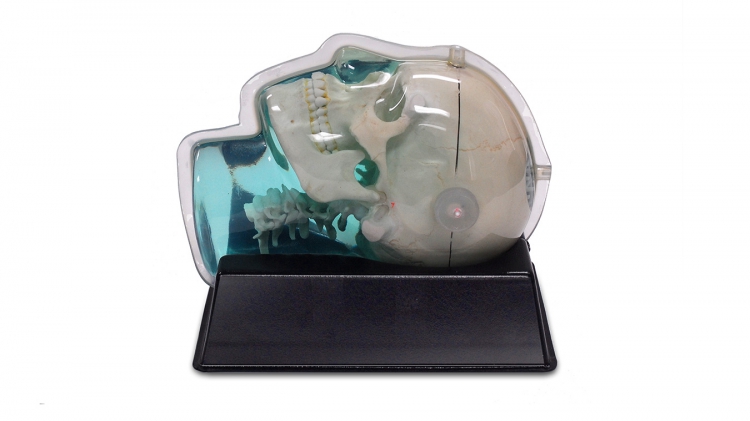
CIRS Model 603A was designed for assessment of MR image distortion in Stereotactic Radiosurgery Planning. It is also a useful tool for verifying image fusion and deformable image registration algorithms used in various treatment planning systems. The tissue equivalent, anthropomorphic design provides the closest conditions to a clinical imaging scenario. The phantom can be imaged using X-ray, Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance. It images well with all MRI sequences tested to date, including T1 weighted, T2 weighted, 3D Time of Flight, MPRAGE and CISS.
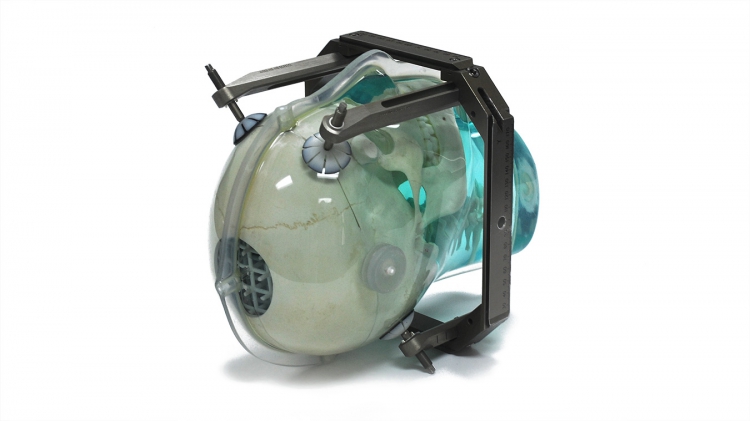
The skull is manufactured from a plastic-based bone substitute, and the interstitial and surrounding soft tissues are made from a proprietary signal generating water-based polymer. The entire phantom is encased in a clear plastic shell to protect gel from desiccation. The phantom is supplied with specially designed pads that allow fixation with any stereotactic frame or mounting for end-to-end testing. The phantom is also suitable for frameless SRS QA.
The entire inter-cranial portion of the skull volume is filled with an orthogonal 3D grid of 3mm diameter rods spaced 15 mm apart. Five extended axis-rods intersect at the reference origin of the grid. The end of each extended axis is fitted with CT/MR markers allowing for accurate positioning with lasers and co-registration of CT and MR image sets.
The phantom includes right and left air voids, 3 mm in diameter by 17 mm long to simulate each ear canal for evaluation of potential distortions commonly found in clinical settings.
To accommodate image fusion techniques, CIRS can offer value added services such as phantom specific CMM, reference CT or MRI data sets, attachment of customer specific registration devices and inclusion of special point markers.
Features:
- Images well on T1, T2 and 3D TOF MRI acquisitions
- Images well on CT scans
-
Protective pad for use with Stereotactic Frame
- Images can be imported into stereotactic localization program
- CT scans can be used to assess MRI accuracy